Everything you need to know about sustainability reporting
Sustainability reporting is gradually becoming mandatory for companies. While the first companies have already started reporting, large and medium-sized companies should consider preparing for the sustainability report.
What does sustainability reporting mean? Why is it suddenly on everyone’s lips? Who is affected and when? How do you collect your data and how do you successfully implement the sustainability report - also known as the ESG report? We answer all your questions about the new sustainability development.
Content:
What does sustainability reporting mean?
Companies as drivers in the field of climate change
Why should companies write a sustainability report?
Which companies are affected when it comes to sustainability reporting?
Basics of sustainability reporting in accordance with the CSRD
All ESG requirements at a glance: What needs to be considered?
This belongs into the introduction of your sustainability report
Main part of your ESG report
Exceptions and innovations to sustainability reporting
Independent auditors
The most important to-dos for your sustainability report
Questions about sustainability reporting?
What does sustainability reporting mean?
The term “sustainability reporting” refers to the mandatory reporting by companies on sustainability aspects as well as impacts and risks in connection with their own business activities. The sustainability report is also known as ESG reporting (Environmental, Social, Governance) or ESG reporting because it deals with the measures and influences relating to sustainability in an ecological, social and economic sense.
Since the new EU CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) came into force in January 2023, stricter rules have applied to company reports. The new reporting standards of the CSRD Directive are intended to achieve better comparability and a quantitative assessment of companies’ sustainability efforts.
Companies as drivers in the field of climate change
Companies are the main cause of climate change. With the new sustainability reporting, sustainable management is no longer a voluntary decision, but the new standard that is to be achieved step by step in all companies. The CSRD directive therefore aims to create a sustainability process that all companies must go through so that our economy can remain in harmony with the environment and future generations in the long term.
Why should companies write a sustainability report?
By examining their structures and their impact on people, the environment and the climate, companies are rethinking the way they do business. And this in turn has many advantages for companies.
Ecologically sustainable: reduction of the ecological footprint
With efficient ESG risk management, companies can counteract climate risks and transitional risks more reliably. Those who develop more climate-friendly and energy-efficient processes and products also increase the value of the company and manage to reduce costs long-term.
The fact that companies are making plans on how they can contribute to climate and environmental protection and reduce their ecological footprint certainly sounds obvious to most people in view of the current crisis. But why is it so important to take social and economic factors into account in sustainability reporting? And what exactly do these have to do with sustainability?
Socially sustainable: building up an inclusive corporate culture
Social sustainability is about establishing a corporate culture that improves productivity long-term. After all, productivity is needed when converting to lower-emission technologies. The term productivity not only means the effective use of resources through work processes, but also the efficient management of human resources. A motivated, involved and well-trained team works much more efficient and innovative and thus contributes to long-term productivity.
Through their sustainability efforts in the context of sustainability reporting, companies therefore establish values that form the basis for a sustainably productive and satisfied team:
- Self-determination
- Participation
- Equality
- Safety and security
- Personal and professional development
- motivation
- Dynamism
- Trust
Economic sustainability: promoting long-term profitability and generating added value
Efficient resource management leads not least to increased economic efficiency and profitability. Social, economic and ecological aspects in a company are closely linked and together contribute to the sustainable and long-term success of a company.
Transparent disclosure of financial performance and risks, for example, cannot only strengthen stakeholder trust, but also help to understand and minimize the company’s impact on the environment and society. Likewise, a long-term mindset that goes beyond short-term profit targets can help to mitigate long-term environmental and social risks and ensure long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
It is therefore important to consider economic, social and environmental aspects in a holistic approach to sustainability in order to ensure long-term success.
Which companies are affected when it comes to sustainability reporting?
Sustainability reporting has been around for some time, but has been tightened up by the new CSRD Directive. Read our blog post to find out how the CSRD Directive came about and how it differs from the NFRD.
Basics of sustainability reporting in accordance with the CSRD
In the sustainability reporting process, companies describe and evaluate measures, progress and targets in the social, environmental and economic areas. Companies are therefore obliged to develop a sustainability strategy that they monitor continuously.
Sustainability reporting: Sustainability strategy goals
The EU Commission stipulates that companies must clearly state which goals they want to achieve with regard to a sustainability strategy. What social standards are they aiming for in order to strengthen values such as safety, satisfaction and participation in their company?
To what extent can emissions be reduced and resource management improved?
What does the company want to do in terms of politics?
Sustainability measures
These measures include all efforts to counteract the advancing climate change and ensure the protection of our environment, fellow human beings and a sustainable economy. These include the reduction of CO2 emissions as well as the active equal distribution of genders in the team or optimizations with a view to more energy-efficient processes. As you can see, the topic of sustainability is wide-ranging. The significance analysis (see below) helps you to narrow down the areas and measures that apply to you.
Progress on sustainability
In the sustainability report, companies describe the progress of the measures they are taking to achieve their own goals. It is about both visible improvements, which are presented using key figures, as well as the presentation of the general process and the activities that have been undertaken.
Try to visualize your data in such a way that the sustainability development can be understood even without data knowledge. Anything that cannot be represented in figures should be described and documented as precisely as possible.
Materiality analysis to define individual sustainability factors
In order to determine the sustainability criteria relevant to the respective company for the report, companies assess the direct and indirect effects of their actions on the environment, climate development, employees, residents and customers in advance. Conversely, current sustainability developments and climate change have an impact on companies and present both risks and opportunities for companies. Both perspectives are examined in the sustainability report. This process is also known as a materiality analysis.
All ESG requirements at a glance: What needs to be considered?
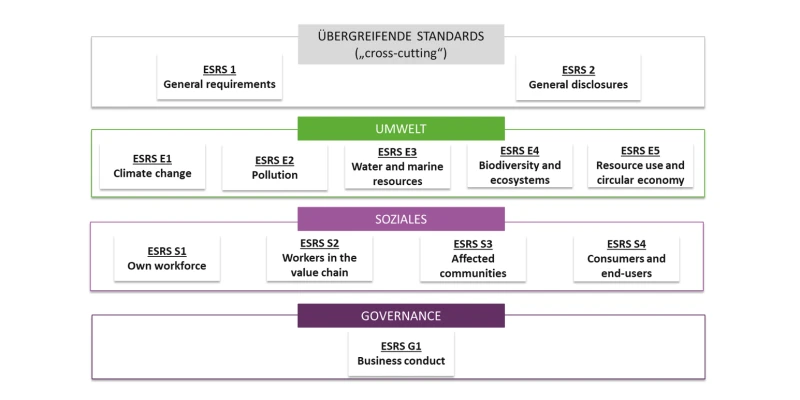
On July 31, 2023, the EU Commission issued specific requirements, the so-called ESRS standards (European Sustainability Reporting Standards), for sustainability reporting. These form the common thread in the evaluation of your sustainability measures.
The 12 ESRS standards for your sustainability report
- ESRS 1 & 2: General data and information
- ESRS E1 Climate change
- ESRS E2 Environmental pollution
- ESRS E3 Water and marine resources
- ESRS E4 Biodiversity and ecosystems
- ESRS E5 Use of resources and circular economy
- ESRS S1 Own workforce
- ESRS S2 Workforce in the value chain
- ESRS S3 Affected communities
- ESRS S4 Consumers and end users
- ESRS G1 Corporate policy
 Source: Federal Environment Agency, 2024
Source: Federal Environment Agency, 2024
Example criteria for the 12 ESRS, we show in our article “ESRS Standards: Requirements & Components of ESG Reporting”.
This belongs into the introduction of your sustainability report
There is a specific order for your sustainability report:
At the beginning of your report, you write an introduction with general details and information about your company. You also explain which sustainability criteria (ESRS) you have chosen after the materiality analysis and why these are particularly relevant for your company.
For the introduction, the various stakeholders in your company and their interests should also be taken into account.
Give guidance to your readers. Show what makes you stand out as a company, that you meet all the requirements for sustainability reporting and how you implement sustainability development in your company.
Main part of your ESG report
In the main part of your sustainability reporting, the relevant ESRSs are processed one after the other. The following process is carried out for all selected ESRS:
- Goals: State a specific and smartly formulated objective for each criteria.
- Risks and impacts: Then, for each criteria, describe both its impact on the environment (meaning the impact on the surroundings and the people with whom the company interacts directly and indirect) and its short-term and long-term impact on your company.
- Sustainability strategy and ESG risk management: Describe your strategy for analyzing, monitoring and managing this criteria. What opportunities await you as part of your sustainability strategy?
- Measures: Show exactly which measures you are implementing to achieve your goals and to what extent you are achieving your goals as a result.
- Controlling: Which key figures do you check in order to measure your sustainability progress? What do controlling and reporting look like in detail? At this point, it is also interesting to know which ESG software you use to measure your progress.
- Results: Share your results and progress using graphs, tables and lists.
- Conclusion: Last but not least, you should prove that your efforts are consistent from start to finish. Add evidence and certificates to your sustainability reporting.
Exceptions and innovations to sustainability reporting
The IHK website provides up-to-date information on so-called transitional provisions. For example, special regulations apply to companies with up to 750 employees. We can assume that further exemptions, additions and revisions to the previous regulation will follow in the months and years to come. On the official website of the European Union, but also on sites such as those of the Chamber of Industry and Commerce, there is continuous information about innovations to the sustainability requirements. You can also follow our LinkedIn channel to keep up to date with all the important information on sustainability reporting, ESG software and ESG controlling.
Independent auditors
While the verification of the sustainability report has so far been voluntary, the CSRD Directive stipulates that an external audit is to become mandatory for large companies in 2025. External auditors are auditing firms in particular. However, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), which published the GRI Standards on sustainability reporting in 2021, also supports you with its own certification courses. The GRI has created a new compliance index with the ESRS standards in accordance with the CSRD, providing a solid basis for companies to use as a guide.
The most important to-dos for your sustainability report
In particular, you will have new work to do when preparing your data as part of sustainability reporting. In our guide „Creating a sustainability report in 9 steps“, we summarize the most important steps for you, from preparation to formulating objectives, data collection, software selection, reporting and reviewing your report.
Questions about sustainability reporting?
Our ESG experts will advise you on the requirements and data collection for your sustainability report. We will find the right planning models and reporting dashboards for your needs.
If you would like to start monitoring the interactions, developments and measures in your company in real time, you can now arrange a free consultation with us or test our controlling and ESG software.


